(Migrated from old blog)
So, I have been taking this course this semester called as Recommendation Systems and the earliest boom this program took was when in 2010 or 2011 Netflix started a competition named as Netflix Prize, it was for $1,000,000.
The Goal of the experiment was to predict the rating a user will give based on the users and movie rating table that was given already.
My teacher gave us a competition on Kaggle : https://www.kaggle.com/c/itmo-rs-autumn2019-track1
The task was to have minimum RMSE on this dataset.
At First, I had no idea what to do then, I decided to atleast create the design matrix. So in Recommendation Systems a design matrix is collection of users by row and movies by columns, it is generally a sparse matrix and is very hard to train.
1
2
3
movies_matrix = training_data.pivot_table(index='user_id', columns='item_id', values='rating')
movies_matrix = movies_matrix.fillna(0)
movies_matrix.head()
This gives an output like the design matrix :
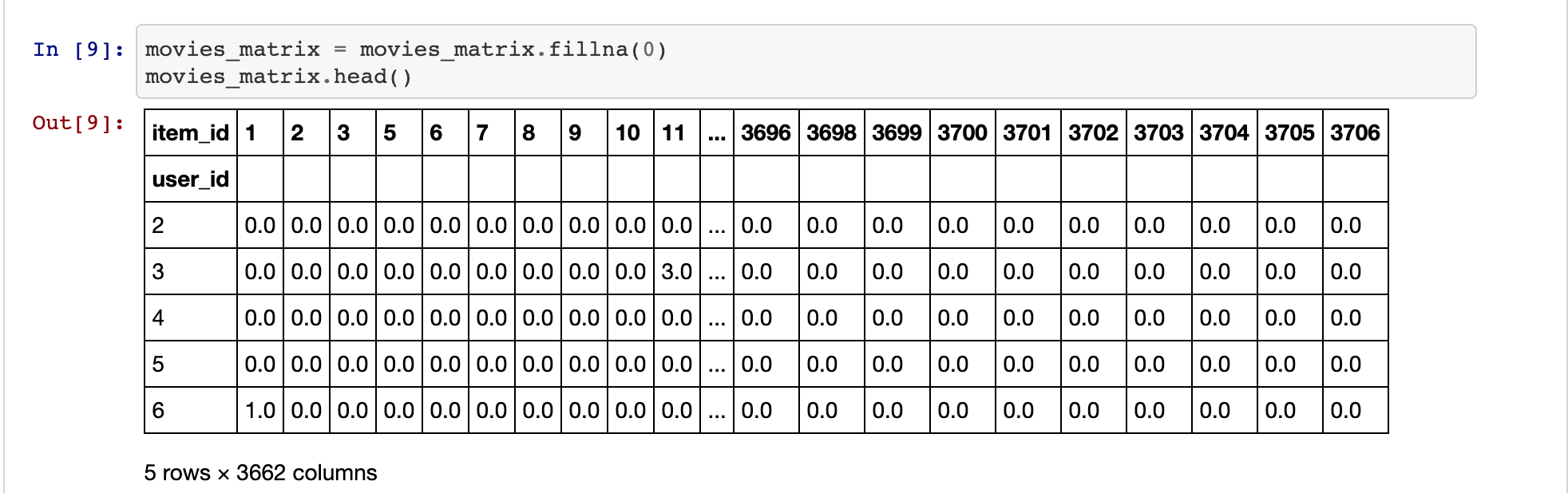 Recommendation System’s Design Matrix
Recommendation System’s Design Matrix
First Approach
It was a very naïve approach, based on a simple idea that If 9 users rated a movie 3 the 10th user will also have a high chance that the movie rating will be three.
So a basic line of code gave me pretty good matrix with item and its average
1
2
training_data = pd.read_csv('../input/itmo-rs-autumn2019-track1/train.csv')
training_data.head()
I calculated the mean of all Items for users
1
2
item_avg_rating_table = pd.DataFrame(training_data.groupby('item_id', as_index=False)['rating'].mean())
item_avg_rating_table
Now a left join of this table with the test data will give me my desired matrix that I need and for those that were not present I changed the value to an average of 3
1
2
3
4
output_table = pd.merge(testing_data, item_avg_rating_table, on='item_id', how='left').loc[:,['Id', 'rating']]
output_table = output_table.rename(columns={'rating' : 'Predicted'})
output_table['Predicted'] = output_table['Predicted'].fillna(3)
output_table.to_csv('submission.csv',index=False)
And like this, my submission got around .9500 RMSE That was a decent score for such a stupid way.
Code can be found here: https://github.com/shivammehta007/RecommendationSystemCodes/blob/master/Netflix%20Prize%20Contest/AverageCase.ipynb
Correct Way: Matrix Factorization or FunkSVD
So one of the IDEAL way to do is to Factorize the Matrix (movie matrix) above and generate latent vectors from there. (Singular Vector Decomposition)
But to do it is a very aweful computation and imagine the size of such matrix for 1000 users and 10000 movies, it will be 1000x10000 and the real world size if way higher.
So Simon Funk one of the winners in the Netflix Competition discovered a cool technique people later called in FunkSVD.
So we take the average and add a delta for each user’s preference eventually, we train that delta preference value using SGD or any other optimization for each user resulting in the value and preference of that user for movies of such types.
Pretty Cool approach its original post was here : https://sifter.org/~simon/journal/20061211.html
So I found a package of doing it instead of approaching it from scratch, Surprize had it but it took a lot of time but this repository used highly optimized numba to optimize it: https://github.com/gbolmier/funk-svd
So I just used it and found a better RMSE of .9300s which made me win the in-class competition :D
1
2
3
4
5
6
recommending_matrix = training_data.loc[ : , ['user_id', 'item_id', 'rating' ]].sort_values('user_id')
recommending_matrix = recommending_matrix.rename(columns={'user_id' : 'u_id', 'item_id': 'i_id'})
recommending_matrix.head()
svd = SVD(learning_rate=0.001, regularization=0.005, n_epochs=100, n_factors=15, min_rating=1, max_rating=5)
svd.fit(X=recommending_matrix, shuffle=False)
pred = svd.predict(testing_data)
You can find my Funk SVD Notebook here : https://github.com/shivammehta25/RecommendationSystemCodes/blob/master/Netflix%20Prize%20Contest/Solution_FunkSVD.ipynb